Mossa M. Marbat, Mohmed abid Ali, Azzawi M. Hadi
Abstract
Infertility is a condition defined by the failure of the wife to achieve a successful pregnancy after 12 months or more of regular unprotected intercourse. About 1 in 7 couples have problems conceiving, with a similar incidence worldwide. Over 80% of couples who have regular sexual intercourse and do not use contraception will achieve a pregnancy within one year. The aim of this was to investigate the effect of Nigella sativa on male infertility. This study is a case-control longitudinal clinical study. It was conducted on 55 infertile men with an age range from 18-40 years from December 2011 to December 2012. The patients included were those who attended the clinics of specialist urologist, who are complaining of infertility with low sperm count or quality. Forty patients from a total of 55 patients (15 patients withdraw from the study for many reasons) who were complete the whole treatment trial were included in this study. 40 infertile men were treated with N. sativa Capsule 2g per day. Semen parameters, serum Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), Luteinizing hormone (LH), and testosterone were measured before and after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa. Sperm count was significantly increased after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa. The percentage of actively moving sperms was significantly increased after 3 months of treatment with N sativa. The semen volume was significantly increased after 3 months of treatment with N sativa. The sperms viability was significantly increased after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa. Sperms normal morphology was significantly increased after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa. Serum FSH, LH, and testosterone levels were significantly increased after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa. These results supported by many studies published that explained and concluded the effect of N. sativa on semen quality. The present study conclude that N. sativa can be used as a single agent for the treatment of male infertility.
Key words:- N. sativa, male infertility, semen parameters, serum FSH, LH and testosterone.
Introduction
Infertility is a common clinical problem affecting 13–15% of couples worldwide. The prevalence varies throughout developed and underdeveloped countries, being higher in the latter in which limited resources for diagnosis and treatment exist. A malefactor is solely responsible for infertility in approximately 20% and contributory in another 30–40% of couples; as such, a malefactor is implicated in more than 50% of couples attempting to conceive (1-2). The use of plants as medicine dates from the earliest years of man’s evolution. Medicinal plants serve as therapeutic alternatives, safer choices, or in some cases, as the only effective treatment. People in different cultures and places have used particular plants to treat certain medical problems. A larger number of these plants and their extract have shown beneficial therapeutic effects, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-microbial effects. Among the promising medicinal plants, Nigella sativa, a dicotyledonous of the Ranunculaceae family, is an amazing herb with a rich historical and religious background, (5-9). Nigella sativa (N. sativa) seed, called as ‘Black Seed’ in English language, ‘Habba Al-Sauda’ or ‘Habba Al-Barakah’ in Arabic, (7). Unfortunately very few of us in the medical profession are aware of its medicinal properties discovered by modern scientific techniques. The aim of this research was to investigate the effect of Nigella sativa on male infertility.
Patients & Methods
This study is a case-control longitudinal clinical study. It was conducted on 55 infertile men with an age range from 18-40 years from December 2011 to December 2012. The patients included were those who attended the clinics of specialist urologist, who are complaining of infertility with low sperm count or quality. Forty patients from a total of 55 patients (15 patients withdraw from the study for many reasons) who were complete the whole treatment trial & were included in this study. Gynecological examination of female partners was done to exclude any female partner causes of infertility. The female subjected to clinical examination and ultrasound and asked about the genetic problems and chronic disease. Then the male partner was recommended to consult a fertility specialist for a complete evaluation. A questionnaire was prepared to obtain the information from the infertile men before semen analysis which includes name, age, job, home and marriage duration, and surgical operation, recent hormonal treatment during the last 6 months, chronic disease, and genetic problem. forty infertile men were treated with N. Sativa Capsules 2g per day (two capsules twice daily). All the hormonal assays were performed in the Salahaddin General hospital using the Minividus apparatus of the biomerieux company. Statistical analysis was done by using an unpaired Student T-test. All data were presented as a mean & standard deviation (SD). P-value less than 0.05 & 0.01 were accepted as significant values.
Results
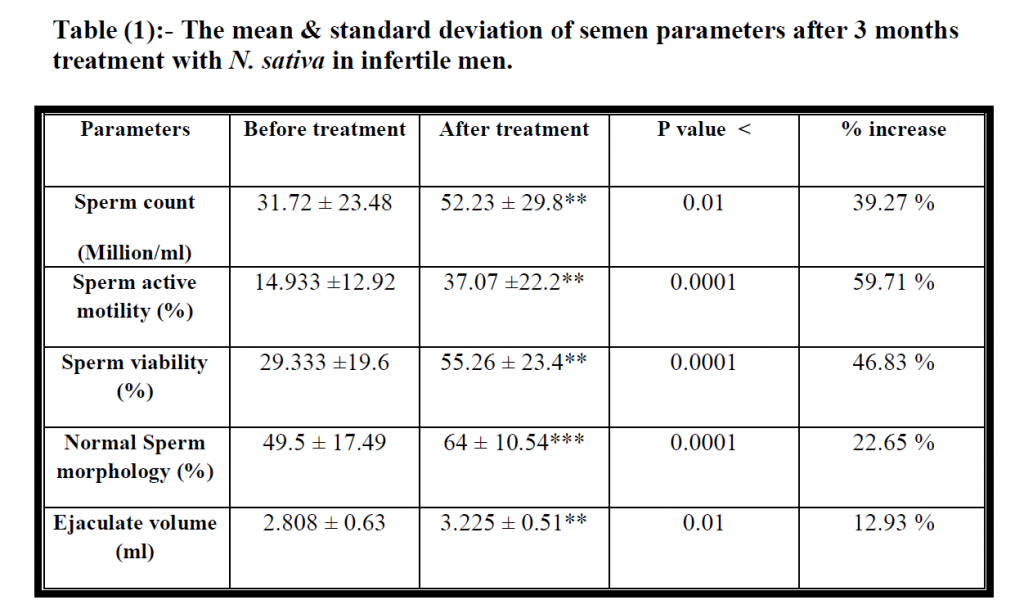
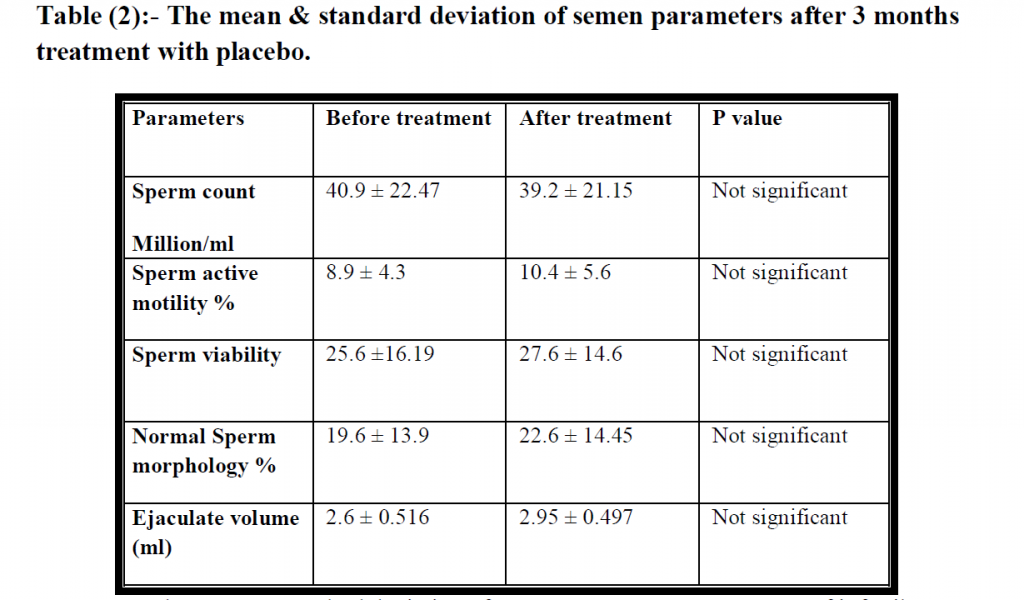
After 3 months of treatments, for 2 groups, the 1st group treated with 2 grams of Nigella Sativa powder per day. While the 2nd group treated with placebo (2 gm wheat bran per day). There is a significant increase in sperm count in infertile men treated with Nigella sativa, and the % of increment in sperm count after three months of treatment 39.27 % (Table 1, figure 1). However, there are non-significant differences in sperm count of the infertile group treated with placebo, (Table 2). Moreover, there is a significant increase in sperm active motility in infertile men treated by Nigella sativa, and the percent of increment in sperm active motility is 59.71%, (Table 1, figure 2). While there is a non-significant increase in sperm active motility in the placebo group after 3 months of treatment with placebo (Table 2). Also, there is a significant increase in sperm viability in infertile men treated with Nigella sativa for 3 months, and there is a 46.83 % increase in sperm viability after treatment as compared with that value before treatment (Table 1, Figure 3). While there is a non-significant increase in sperm viability in the placebo group after 3 months of treatment with placebo (Table 2). Moreover, there is a significant increase in normal sperm morphology in infertile men treated with Nigella sativa for 3 months, and there is a
22.65% increase in sperm viability after treatment as compare with that value before treatment (Table 1, figure 4). While, there is non significant increased in normal sperm morphology in placebo group after 3 months of treatment with placebo, (Table 2).
There is a significant increase in ejaculate volume in infertile men treated with Nigella sativa for 3 months, and there is a 12.93 % increase in ejaculate volume after treatment as compared with that value before treatment, (Table 1, figure 5). While there is a non-significant increase in ejaculate volume in the placebo group after 3 months of treatment with placebo (Table 2).
Serum hormones of infertile men There is a significant increase in serum FSH in infertile men after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa (2 gm per day). The percent of increment in serum FSH is 47.46 %, (table 4, figure 6). There is a significant increase in serum LH in infertile men after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa (2 gm per day). The percent of increment in serum LH is 32.75 %, (table 4, figure 7). There is a significant increase in serum testosterone in infertile men after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa (2 gm per day). The percent of increment in serum testosterone is 29.35 %, (table 4, figure 8).
Discussion
In the present study, there is a significant increase in sperm count, sperm active motility, sperm viability, normal sperm morphology, & ejaculate volume in infertile men treated with Nigella sativa, and the % of increment in sperm count after three months of treatment was 39.27 %, (table 1). However, there is non-significant differences in sperm count, sperm active motility, sperm viability, normal sperm morphology & ejaculate volume of the infertile group treated with placebo,
(Table 2). Several studies were carried out to demonstrate the effect of certain plants and herbs extract on mammalian fertility, some of these studies attributed the improvement to FSH and LH induction level (7,9,11). Hyperlipidemia may associated with impaired semen quality, (12-13), administration of N. sativa cause a reduction in serum lipid & improve in semen parameters in Albino rat, (12, 13, 15). In the present study, there is significant increase in serum FSH, LH & testosterone in infertile men after 3 months of treatment with N. sativa (2 gm per day). Nigella sativa oil supplementation in 0.3 cc dosage to alloxan induced diabetic mice cause an increase in sperm motility (16). Also, daily oral administration of 0.5 and 1.5 g/Kg B.W of alcoholic extract of Nigella sativa L. for 53 days lead to clear improvement of male rats fertility, (17). Also, in experimental animal, supplement of N. sativa lead to increase in testosterone level, (17- 18). The cause of testosterone hormone increment may be due to the effect of black seed on the main enzymes which affect the metabolism and steroid secretion in the testis. The increase in sperm concentration was due in part to the increase in testosterone and FSH levels in testicular tissue, since these two hormones were responsible for spermatocytogenesis and spermiogenesis in seminiferous tubules, while testosterone is responsible for epididymal function in maturation of sperms (19). The results of the present study were in agreement with previous studies done on animals which reported that black seed contains alkaloids and phenols which stimulate the secretion of FSH and testosterone, (19-20). The results of Parandin1 Rahmatollah et al study (2011) showed that alcoholic extract of Nigella sativa seeds especially in higher doses could increase fertility in male rats. There was a significant increase in testes and epididymis weight, sperm count, serum testosterone, FSH and LH concentrations in both the lower dose group and the higher dose group of N. sativa as compared to the control group, (21). In another study, the effect of Nigella sativa oil was studied on male rat, & it was found N. sativa oil extract induced a significant increase in the weight of reproductive organs, and in the circulating levels of serum FSH, LH & testosterone as compared to control animals (P< 0.05). The study concluded that the Nigella sativa fixed oil may stimulate steroidogenesis by activation of hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis, (22). Recently, an Iraqi study was done to investigate the effects of Nigella sativa oil on the reproductive system of rats. The treated animal (1ml/kg/day for 30 days) showed significant increases in total protein and significant decreases in total cholesterol. Significant increases in the levels of LH, FSH and testosterone for males and LH, FSH, estrogen and progesterone for females were recorded in treated rat with N. sativa, (23). Also, a study was done in Jordan to investigate the effect of N. sativa on male albino rat’s reproductive systems. Spermatogenesis was increased at primary & secondary spermatocyte stages. Epididymides showed an elevated number of spermatozoa. Treated rat’s testicular cell population showed an increase in the number of spermatocytes and spermatids (P<0.001) when compared to control animals. It is concluded that the aqueous extracts of Nigella sativa have increased spermatogenesis of male albino rats, (24). The process of spermatogenesis and accessory reproductive organs function are androgen-dependent. In this study the number of mature Leydig cells were significantly increased. This reflects
the increase of androgen level. It is further confirmed by the increased number of spermatocytes (primary and secondary) and spermatids as these stages are completely androgen-dependent (24). In one study done in Tikrit by using high performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) analysis, a 12 flavonoids were indicated & only seven were identified. The identified flavonoids included: Catechin, Merictin, Rutin, Hydroxy Quercetin, Kaempherol, Quercetin and Hesperdin at a level of 77.34, 52.3, 47.3, 396.0, 95.6, 267.5, 36.56 μg/ml of extract respectively, (25). Also, N. sativa was extract & given orally in a single daily dose of flavonoid to immature female mice. It was found a significant increase during the second weeks of treatment in groups that received 40, 50, and 60 mg/kg B.W as compared to 20 and 30 mg/kg B.W. flavonoid treated, (26). From the present study, we conclude that there is a significant increase in testosterone levels after treatment with N. sativa may be attributed to somehow, enhancing FSH and LH release, which leads to improvement in all semen parameters. The present study recommends to use N. sativa as single treatment for male infertility or in (complementation) with other therapy.
Refrence:
Marbat MM, Ali MA, Hadi AM. 2013. The use of Nigella sativa as a single agent in the treatment of male infertility. Tikrit J Pharma Sci. 9:19–29

